
|
|
P-E RATIO: Also termed the price-earnings ratio, this is the ratio of the current price for one share of corporate stock to the earnings (profit) per share of stock. This is used by many financial analysts and investors as an indicator of a company's performance and potential for future growth. A relatively high price-earnings ratio suggests that investors think the company has a great deal of future growth potential. It can also be a sign, however, that the company is seriously overpriced and due for a big drop.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           INTERCEPT, SAVING LINE: The intercept of the saving line indicates autonomous saving, saving that does not depend on the level of income or production. This can be thought of as the baseline level of saving that would be undertaken if income falls to zero. Autonomous saving is affected by the consumption expenditures determinants, which cause a change in the intercept and a shift of the saving line. The value of the intercept of the saving line is the negative of the value of the intercept of the consumption line. | Saving Line | 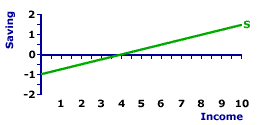
|
The saving line, also termed propensity-to-save line or saving function, shows the relation between saving and income for the household sector. The income measure commonly used is national income or disposable income. Occasionally a measure of aggregate production, such as gross domestic product, is used instead.A representative saving line is presented in the exhibit to the right. This green line, labeled S in the exhibit, is positively sloped, indicating that greater levels of income generate greater saving by the household sector. This positive relation corresponds to the fundamental psychological law of Keynesian economics. The saving line graphically illustrates the saving-income relation for the household sector, which is the foundation of the leakages line used in Keynesian economics to identify equilibrium income and production. The intercept of the saving line indicates the intersection point between the saving line and the vertical saving axis. The saving line intersects the vertical axis at a value of -$1 trillion. Theoretically, this is a minimum "baseline" level of saving, the amount of saving undertaken if income falls to zero. This level happens to be negative because consumption exceeds income. More to the point, this intersection indicates autonomous saving--saving unrelated to income. Click the [Intercept] button to illustrate. Autonomous saving is saving by the household sector that is unrelated to and unaffected by the level of income or production. This is best indicated by a zero level of income. While individuals occasionally come face-to-face with autonomous saving, as their incomes drop to zero due to unemployment, for the aggregate economy autonomous saving is mostly an unlikely theoretical extrapolation. However, from an analytical perspective, the intercept of the saving line is affected by the consumption expenditures determinants. These are ceteris paribus factors other than income that affect consumption and thus also affect saving, but which are held constant when the saving line is constructed. Any change in these determinants cause the saving line to shift, which necessarily means a new intercept and a new level of autonomous saving.

Recommended Citation:INTERCEPT, SAVING LINE, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 13, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
GREEN LOGIGUIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time browsing through a long list of dot com websites looking to buy either handcrafted decorations to hang on your walls or throw pillows for your bed. Be on the lookout for the last item on a shelf.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
In 1914, Ford paid workers who were age 22 or older $5 per day -- double the average wage offered by other car factories.
|

|
|
"We can't take any credit for our talents. It's how we use them that counts. " -- Madeleine L'Engle, Writer
|

|
BEA
Bureau of Economic Analisys
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


